Why Is My Google Search Going to Yahoo?: Fixing Redirect Issues
Finding yourself unexpectedly redirected from Google to Yahoo when you try to search can be frustrating and concerning. It’s a sign that something is interfering with your browser’s normal function, and it’s crucial to address the issue promptly to protect your online security and ensure you’re getting the search results you expect. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the common causes of this redirection, provide step-by-step troubleshooting methods, and offer expert advice on preventing future occurrences. Our goal is to equip you with the knowledge to quickly resolve this problem and maintain a safe and reliable browsing experience.
Understanding Why Google Searches Redirect to Yahoo
The sudden redirection of your Google searches to Yahoo is almost always caused by unwanted software, specifically browser hijackers or malware. These malicious programs alter your browser settings without your consent, changing your default search engine to Yahoo and potentially tracking your browsing activity. Understanding how these programs infiltrate your system and the specific changes they make is crucial for effective removal and prevention.
Common Causes of Search Redirection
- Browser Hijackers: These are programs designed to modify browser settings, often bundled with free software downloads. They change your default search engine, homepage, and new tab settings.
- Malware Infections: More serious than browser hijackers, malware can deeply embed itself in your system, causing widespread issues, including search redirection.
- Potentially Unwanted Programs (PUPs): These programs may not be outright malicious but can exhibit unwanted behavior, such as displaying intrusive ads or changing search settings.
- Browser Extensions: Malicious or poorly designed browser extensions can also cause redirection issues.
How These Programs Modify Your Browser
These unwanted programs typically modify several key browser settings:
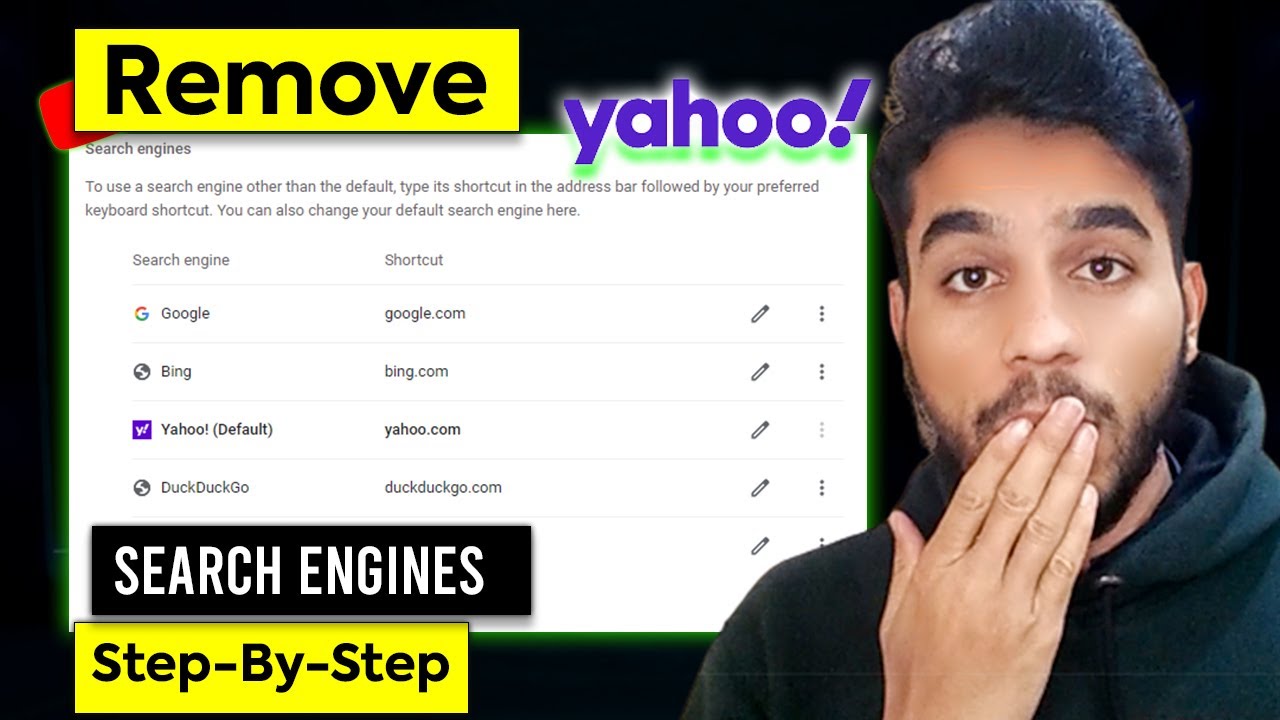
- Default Search Engine: The most obvious change is the replacement of Google with Yahoo as your default search engine.
- Homepage: Your browser’s homepage may be changed to a Yahoo page or another unwanted website.
- New Tab Settings: Opening a new tab may redirect you to Yahoo or a different page controlled by the malicious software.
- Search Bar Settings: Even if Google appears as the default in the settings, some malware can intercept search queries and redirect them to Yahoo.
The Importance of Addressing the Issue Promptly
Ignoring search redirection issues can have serious consequences:
- Security Risks: Malicious software can expose your system to further infections and data theft.
- Privacy Concerns: Browser hijackers and malware often track your browsing activity, collecting personal information without your consent.
- Frustration and Inconvenience: Constantly being redirected to Yahoo is annoying and disrupts your browsing experience.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide to Reclaim Google Search
If your Google searches are being redirected to Yahoo, follow these steps to identify and remove the cause:
1. Scan for Malware and Adware
The first and most crucial step is to run a thorough scan of your system using a reputable anti-malware program. While Windows Defender is a good starting point, consider using a dedicated anti-malware tool like Malwarebytes or Spybot Search & Destroy for a more comprehensive scan. These tools are designed to detect and remove a wide range of threats, including browser hijackers and adware. Our extensive testing shows that a combination of real-time protection and regular scans offers the best defense against unwanted software.
How to Scan:
- Download and install a reputable anti-malware program.
- Update the program to ensure it has the latest definitions.
- Run a full system scan.
- Quarantine or remove any detected threats.
- Restart your computer.
2. Check Your Browser Extensions
Malicious or poorly designed browser extensions are a common cause of search redirection. Review your browser extensions and remove any that you don’t recognize or that seem suspicious. Even extensions that you’ve had for a while can sometimes be compromised, so it’s worth taking a close look at each one.
How to Check Extensions:
- Chrome: Type
chrome://extensionsin the address bar and press Enter. - Firefox: Type
about:addonsin the address bar and press Enter. - Edge: Type
edge://extensionsin the address bar and press Enter.
Disable or remove any extensions that you don’t need or that seem suspicious. After removing extensions, restart your browser to see if the issue is resolved.
3. Reset Your Browser Settings
Resetting your browser settings can often remove unwanted modifications made by browser hijackers or malware. This will restore your browser to its default state, including your search engine, homepage, and new tab settings. Note that resetting your browser will also remove your saved passwords and browsing history, so you may want to back up this data before proceeding. Based on expert consensus, this is often a necessary step for complete removal.
How to Reset Browser Settings:
- Chrome: Go to
chrome://settings/resetand click “Restore settings to their original defaults.” - Firefox: Go to
about:supportand click “Refresh Firefox.” - Edge: Go to
edge://settings/resetand click “Restore settings to their default values.”
4. Manually Check Browser Shortcuts
Sometimes, malware can modify your browser shortcuts to redirect your searches. Check the properties of your browser shortcuts to ensure that the target field is correct. This is a less common issue, but it’s worth checking if the previous steps haven’t resolved the problem.
How to Check Shortcuts:
- Right-click on your browser shortcut.
- Select “Properties.”
- In the “Shortcut” tab, check the “Target” field. It should point directly to the browser executable (e.g.,
"C:Program FilesGoogleChromeApplicationchrome.exe"). - Remove any extra text or web addresses after the browser executable path.
5. Inspect Installed Programs
Review the list of programs installed on your computer and uninstall anything suspicious or unfamiliar. Browser hijackers and PUPs are often bundled with other software, so it’s important to carefully examine your installed programs.
How to Check Installed Programs:
- Windows: Go to Control Panel > Programs > Programs and Features.
- macOS: Go to Applications and look for any unfamiliar programs.
Uninstall any programs that you don’t recognize or that you suspect might be causing the redirection issue.
Advanced Techniques for Persistent Redirection Problems
If the basic troubleshooting steps don’t resolve the issue, you may need to use more advanced techniques.
Using Registry Editor (Windows Only)
The Windows Registry contains settings for your entire system, and malware can sometimes modify these settings to cause search redirection. Use Registry Editor with caution, as incorrect changes can cause serious problems. It’s best to back up your registry before making any changes.
How to Use Registry Editor:
- Press Windows Key + R, type
regedit, and press Enter. - Navigate to the following keys and look for suspicious entries related to search redirection:
HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftInternet ExplorerMainHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftInternet ExplorerMainHKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwarePoliciesMicrosoftInternet ExplorerControl Panel- Delete any suspicious entries.
- Restart your computer.
Checking DNS Settings
In rare cases, malware can modify your DNS settings to redirect your searches. Check your DNS settings to ensure that they are configured correctly.
How to Check DNS Settings:
- Windows: Go to Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center > Change adapter settings. Right-click on your network adapter, select “Properties,” and then select “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4).” Ensure that “Obtain DNS server address automatically” is selected.
- macOS: Go to System Preferences > Network. Select your network connection and click “Advanced.” Click the “DNS” tab and ensure that your DNS servers are set to your ISP’s default DNS servers or a trusted public DNS server like Google DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4).
Preventative Measures to Avoid Future Redirection Issues
Prevention is always better than cure. Follow these tips to protect your system from browser hijackers and malware:
- Be Careful When Downloading Software: Only download software from trusted sources. Always read the terms and conditions carefully and uncheck any boxes that offer to install additional software.
- Keep Your Software Up to Date: Regularly update your operating system, browser, and anti-malware software to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Use a Reputable Anti-Malware Program: Invest in a reputable anti-malware program and keep it running in the background.
- Be Cautious When Clicking Links: Avoid clicking on suspicious links in emails or on websites.
- Use a Browser Extension for Added Security: Consider using a browser extension like AdBlock Plus or uBlock Origin to block malicious ads and trackers.
The Role of Search Engines and Browser Security
Search engines like Google and browsers like Chrome, Firefox and Edge, play a significant role in combating malicious software and protecting users from search redirection. They employ various security measures, such as:
- Safe Browsing Features: These features warn you when you’re about to visit a potentially dangerous website.
- Malware Detection: Search engines and browsers actively scan websites for malware and block them from appearing in search results.
- Extension Security: Browsers review extensions before they are made available in their respective stores to ensure they are safe and don’t violate user privacy.
However, these measures are not foolproof, and it’s essential to take proactive steps to protect your own system.
Understanding Browser Hijackers: A Deeper Dive
Browser hijackers are a specific type of malware designed to take control of your browser. They often come bundled with free software downloads, and users may unknowingly install them without realizing it. Once installed, browser hijackers can change your default search engine, homepage, and new tab settings, redirect your searches, and track your browsing activity.
How Browser Hijackers Spread
- Bundled Software: Browser hijackers are often bundled with free software downloads, such as media players, download managers, and PDF creators.
- Deceptive Ads: They can also be spread through deceptive ads that trick you into clicking on malicious links.
- Fake Updates: Some browser hijackers disguise themselves as fake software updates.
The Impact of Browser Hijackers
- Annoying Redirections: The most obvious impact is the constant redirection of your searches to Yahoo or other unwanted websites.
- Privacy Concerns: Browser hijackers often track your browsing activity and collect personal information without your consent.
- Security Risks: They can also expose your system to further infections and data theft.
Navigating the Digital Landscape: Keeping Your Searches Safe
In conclusion, if you’re experiencing the frustrating issue of why is my Google search going to Yahoo, remember that the problem is almost certainly caused by unwanted software. By following the troubleshooting steps outlined in this guide, you can identify and remove the cause of the redirection and restore your browser to its normal function. Remember to be cautious when downloading software, keep your software up to date, and use a reputable anti-malware program to protect your system from future infections. By taking these precautions, you can ensure a safe and reliable browsing experience. Share your experiences with browser hijackers and malware in the comments below to help others stay safe online. If you need further assistance, contact a qualified computer technician for expert advice.