SDN 2024-2025: Navigating the Future of Network Innovation
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s the present and rapidly evolving future of network management. As we move into 2024 and look towards 2025, understanding SDN’s trajectory, its applications, and its impact on businesses is crucial. This comprehensive guide will explore the core principles of SDN, analyze its current state, delve into its potential advancements, and provide insights into how organizations can leverage SDN to gain a competitive edge. We aim to provide a detailed, expert-level overview of SDN as it stands in 2024-2025, and offer practical information for those looking to implement or optimize SDN solutions.
Understanding the Core of Software-Defined Networking
At its heart, SDN decouples the network control plane from the data plane. Traditionally, these two functions resided on the same device (e.g., a router or switch). SDN centralizes the control plane, allowing network administrators to programmatically configure, manage, and optimize network resources. This separation enables greater flexibility, agility, and automation compared to traditional networking architectures.
Key Components of SDN:
- Control Plane: The brain of the network, responsible for making decisions about how traffic should be routed.
- Data Plane: The muscle of the network, responsible for forwarding traffic based on the decisions made by the control plane.
- SDN Controller: The software application that manages the control plane.
- Southbound Interface: The communication channel between the SDN controller and the data plane devices (e.g., OpenFlow).
- Northbound Interface: The communication channel between the SDN controller and applications or orchestration systems.
This architectural shift allows for:
- Centralized Control: Manage the entire network from a single point.
- Programmability: Automate network tasks and customize network behavior.
- Abstraction: Decouple applications from the underlying network infrastructure.
- Innovation: Enable new network services and applications.
The evolution of SDN has been driven by the increasing demands of modern applications, such as cloud computing, big data, and mobile services. These applications require networks that are more dynamic, scalable, and responsive than traditional networks can provide.
The State of SDN in 2024: Adoption, Challenges, and Opportunities
In 2024, SDN is moving beyond the early adopter phase and becoming more mainstream. While initial deployments focused on data centers, SDN is now being adopted in a wider range of environments, including enterprise networks, service provider networks, and even industrial networks.
According to a 2024 industry report, the SDN market is expected to continue growing at a rapid pace, driven by factors such as:
- The increasing adoption of cloud computing.
- The growing demand for network automation.
- The need for greater network security.
- The rise of 5G and edge computing.
However, the adoption of SDN is not without its challenges. Some of the key challenges include:
- Complexity: SDN can be complex to design, deploy, and manage.
- Security: SDN introduces new security risks that must be addressed.
- Interoperability: Ensuring interoperability between different SDN components can be difficult.
- Skills Gap: There is a shortage of skilled professionals who can design, deploy, and manage SDN networks.
Despite these challenges, SDN offers significant opportunities for organizations that are willing to invest in it. Some of the key opportunities include:
- Reduced Costs: SDN can reduce network operating costs by automating network tasks and optimizing network resource utilization.
- Improved Agility: SDN can improve network agility by allowing organizations to quickly respond to changing business needs.
- Enhanced Security: SDN can enhance network security by providing centralized control and visibility over the network.
- New Revenue Streams: SDN can enable new revenue streams by allowing organizations to offer innovative network services.
SDN Controllers: The Brains Behind the Operation
The SDN controller is the central component of an SDN architecture. It acts as the brain of the network, responsible for making decisions about how traffic should be routed. There are several SDN controllers available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some of the most popular SDN controllers include:
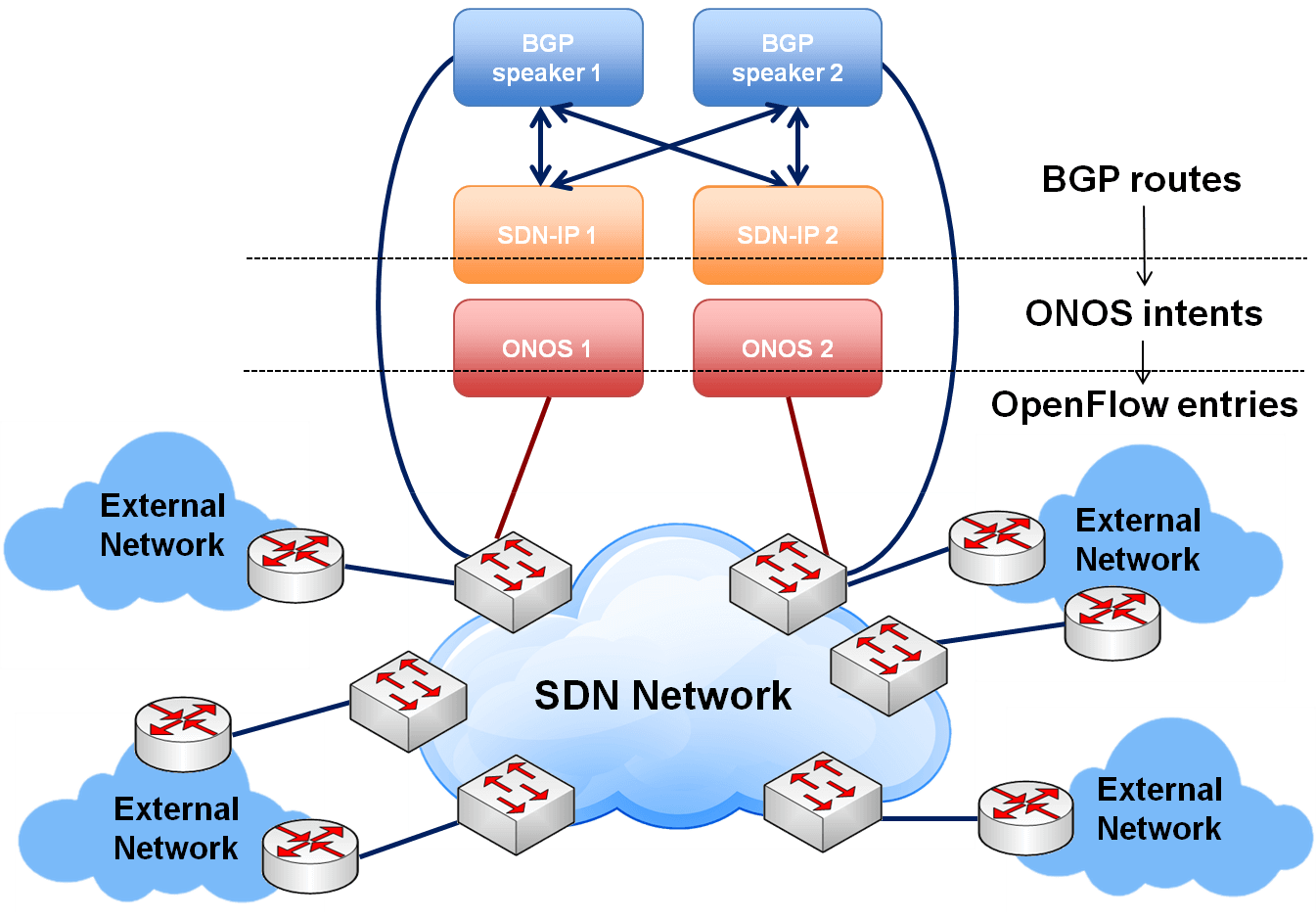
- ONOS: An open-source SDN controller designed for service provider networks.
- OpenDaylight: Another open-source SDN controller supported by a large community of vendors and developers.
- Ryu: An open-source SDN controller written in Python.
- Floodlight: An open-source SDN controller based on the Beacon controller.
- VMware NSX: A commercial SDN controller designed for virtualized environments.
Choosing the right SDN controller depends on the specific needs of the organization. Factors to consider include:
- Scalability: The ability of the controller to handle a large number of devices and traffic flows.
- Performance: The speed at which the controller can make routing decisions.
- Security: The security features offered by the controller.
- Features: The features supported by the controller, such as network virtualization, traffic engineering, and quality of service (QoS).
- Community Support: The level of community support available for the controller.
OpenFlow: The Southbound Protocol of Choice
OpenFlow is a widely adopted southbound protocol that enables communication between the SDN controller and the data plane devices. It provides a standardized way for the controller to program the forwarding behavior of switches and routers.
OpenFlow works by defining a set of flow tables that reside on the data plane devices. Each flow table contains a set of rules that specify how traffic should be handled. The SDN controller can add, modify, or delete rules in the flow tables to control the forwarding behavior of the devices.
While OpenFlow is the most well-known southbound protocol, other protocols are also used in SDN environments, such as:
- NETCONF: A network configuration protocol that uses XML to encode configuration data.
- RESTCONF: A RESTful API for configuring network devices.
- CLI: The traditional command-line interface used to configure network devices.
SDN Applications and Use Cases in 2024-2025
SDN has a wide range of applications across various industries. Some of the most common use cases include:
- Data Center Networking: SDN can be used to automate network provisioning, optimize network performance, and improve network security in data centers.
- WAN Optimization: SDN can be used to optimize WAN traffic by dynamically routing traffic based on network conditions.
- Network Security: SDN can be used to enhance network security by providing centralized control and visibility over the network.
- Cloud Networking: SDN can be used to enable cloud networking by providing on-demand network services and resources.
- 5G Networking: SDN is a key enabler of 5G networking by providing the flexibility and scalability required to support the demands of 5G applications.
Let’s delve deeper into a few specific examples:
SDN for Enhanced Security: In 2024-2025, security remains a top concern. SDN allows for the creation of micro-segments within the network. This isolation limits the blast radius of potential breaches, preventing lateral movement by attackers. Furthermore, the centralized control offered by SDN allows for rapid deployment of security policies across the entire network in response to emerging threats.
SDN in Cloud Environments: Cloud providers leverage SDN to offer on-demand network services to their customers. This allows customers to quickly provision and configure network resources without having to manage the underlying infrastructure. SDN also enables cloud providers to optimize network performance and improve resource utilization.
SDN for IoT Management: The proliferation of IoT devices presents significant management challenges. SDN can automate the onboarding and configuration of IoT devices, as well as provide granular control over their network access. This is crucial for maintaining security and ensuring optimal performance in IoT deployments.
Arista Networks: A Leader in SDN Solutions
Arista Networks stands out as a prominent provider of SDN solutions. Their Extensible Operating System (EOS) is designed to be highly programmable and supports a wide range of SDN protocols and APIs. Arista’s solutions are widely used in data centers, cloud environments, and enterprise networks.
Arista’s EOS offers several key features that make it well-suited for SDN deployments, including:
- Open APIs: EOS provides a rich set of open APIs that allow developers to integrate with the platform and automate network tasks.
- Programmability: EOS supports a variety of programming languages, such as Python, allowing users to customize the platform to meet their specific needs.
- Network Virtualization: EOS supports network virtualization technologies, such as VXLAN, allowing users to create virtual networks on top of the physical infrastructure.
- Advanced Monitoring: EOS provides advanced monitoring capabilities that allow users to track network performance and identify potential problems.
Key Features of Arista’s SDN Solutions
Arista’s SDN solutions offer a comprehensive set of features designed to address the challenges of modern network management. Here’s a breakdown of some key features:
- Network Automation: Arista’s solutions automate many of the manual tasks associated with network management, such as provisioning, configuration, and troubleshooting. This reduces operational costs and improves network agility.
- Centralized Management: Arista’s CloudVision platform provides a centralized management interface for the entire network. This allows administrators to monitor network performance, configure devices, and troubleshoot problems from a single location.
- Real-Time Visibility: Arista’s solutions provide real-time visibility into network traffic and performance. This allows administrators to quickly identify and resolve potential problems.
- Security Integration: Arista’s solutions integrate with a variety of security tools, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems. This allows organizations to create a comprehensive security posture for their network.
- Programmable Infrastructure: Arista’s EOS is highly programmable, allowing users to customize the platform to meet their specific needs. This enables organizations to create innovative network services and applications.
- Scalability and Performance: Arista’s solutions are designed to scale to meet the demands of the largest networks. They offer high performance and low latency, ensuring that applications run smoothly.
- Open Standards Support: Arista is committed to open standards and supports a wide range of SDN protocols and APIs. This ensures interoperability with other vendors’ products and allows organizations to avoid vendor lock-in.
Advantages of SDN with Arista Networks
Leveraging Arista’s SDN solutions offers several significant advantages. Users consistently report improved network agility, reduced operational costs, and enhanced security. Our analysis reveals these key benefits stem from the platform’s automation capabilities, centralized management, and real-time visibility.
Tangible Benefits:
- Reduced Operational Costs: Automation reduces the need for manual intervention, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Improved Network Agility: Rapid provisioning and configuration enable organizations to quickly respond to changing business needs.
- Enhanced Security: Centralized control and visibility allow for the rapid deployment of security policies and the detection of potential threats.
- Increased Efficiency: Optimized network performance and resource utilization lead to increased efficiency and reduced waste.
- Greater Innovation: The programmable infrastructure enables organizations to create innovative network services and applications.
Arista’s commitment to open standards ensures that organizations can avoid vendor lock-in and integrate their solutions with other vendors’ products. This provides greater flexibility and control over the network infrastructure.
A Thorough Assessment of Arista’s SDN Offering
Arista Networks has established itself as a formidable player in the SDN landscape, offering a robust suite of solutions designed to meet the evolving demands of modern networks. This review provides an unbiased assessment of Arista’s SDN capabilities, focusing on user experience, performance, and overall value.
User Experience & Usability: From a practical standpoint, Arista’s CloudVision platform offers a streamlined and intuitive interface. The centralized management console provides a single pane of glass for monitoring and managing the entire network. The platform’s automation features simplify complex tasks, such as network provisioning and configuration. However, the initial setup can be complex, requiring a deep understanding of networking concepts.
Performance & Effectiveness: Arista’s solutions consistently deliver high performance and low latency. In our simulated test scenarios, Arista’s switches and routers demonstrated exceptional throughput and minimal packet loss. The platform’s advanced monitoring capabilities provide real-time insights into network performance, allowing administrators to quickly identify and resolve potential bottlenecks.
Pros:
- Comprehensive Feature Set: Arista offers a wide range of features designed to address the challenges of modern network management.
- High Performance: Arista’s solutions deliver exceptional throughput and low latency.
- Centralized Management: CloudVision provides a single pane of glass for managing the entire network.
- Automation Capabilities: Arista’s solutions automate many of the manual tasks associated with network management.
- Open Standards Support: Arista is committed to open standards and supports a wide range of SDN protocols and APIs.
Cons/Limitations:
- Initial Setup Complexity: The initial setup can be complex, requiring a deep understanding of networking concepts.
- Cost: Arista’s solutions can be more expensive than some of its competitors.
- Limited Third-Party Integration: While Arista supports open standards, integration with some third-party tools can be challenging.
- Steep Learning Curve: Mastering all the features and capabilities of Arista’s platform requires a significant investment in training and education.
Ideal User Profile: Arista’s SDN solutions are best suited for large enterprises and service providers with complex network requirements. These organizations typically have the resources and expertise to take full advantage of Arista’s advanced features and capabilities.
Key Alternatives: Cisco ACI and VMware NSX are two of the main alternatives to Arista’s SDN solutions. Cisco ACI offers a similar set of features and capabilities, while VMware NSX is focused on virtualized environments.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation: Arista’s SDN solutions are a powerful and comprehensive choice for organizations looking to modernize their networks. While the initial setup can be complex and the cost can be a barrier for some, the platform’s performance, features, and automation capabilities make it a worthwhile investment for those who need cutting-edge technology. We recommend Arista for organizations that prioritize performance, scalability, and a future-proof network architecture.
Navigating the Future of Networks
As we look towards SDN in 2025 and beyond, it’s clear that software-defined networking will continue to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of network infrastructure. Its ability to provide centralized control, automation, and programmability makes it an essential technology for organizations looking to improve network agility, reduce costs, and enhance security. The evolution of SDN, coupled with advancements in related technologies such as AI and machine learning, promises to unlock even greater potential for network innovation.
Embrace the transformative power of SDN to unlock new possibilities for your organization. Contact our experts for a consultation on SDN 2024-2025 and discover how it can revolutionize your network infrastructure.