Decoding Smudge Cells: A Comprehensive Guide for Clinicians and Researchers
Smudge cells, also known as basket cells, are intriguing yet often misunderstood entities observed in hematology. Their presence in blood smears can be a diagnostic clue, pointing towards a range of conditions, most notably chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). However, their significance extends beyond CLL, requiring careful interpretation within the broader clinical context. This article provides an in-depth exploration of smudge cells, delving into their origin, clinical relevance, diagnostic implications, and the latest research shaping our understanding. Our goal is to equip clinicians, researchers, and students with a comprehensive resource that goes beyond basic definitions, fostering a deeper appreciation for the nuanced role of smudge cells in hematological assessments.
Unveiling the Nature of Smudge Cells
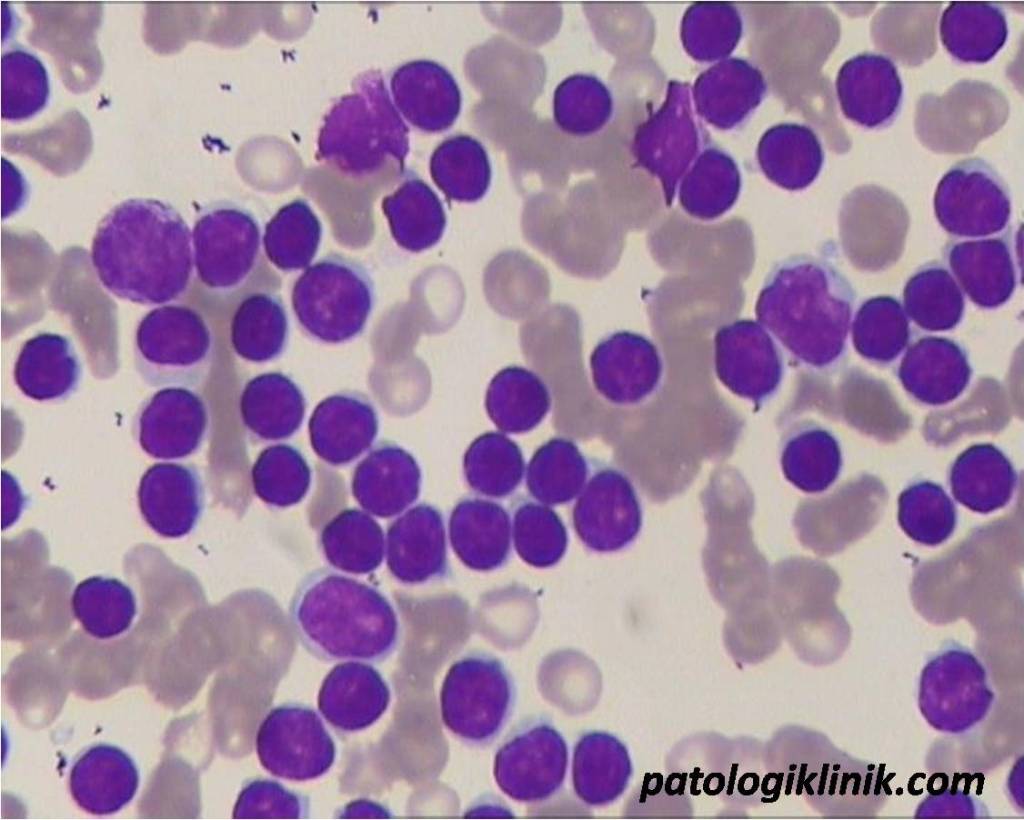
Smudge cells are essentially the remnants of fragile leukocytes (white blood cells) that have ruptured during the process of preparing a blood smear. The mechanical stress of smearing the blood across the slide causes these cells to disintegrate, leaving behind a smudged or smeared appearance. Unlike healthy, robust cells that withstand the smearing process, smudge cells lack structural integrity due to inherent weaknesses or underlying pathological conditions. They appear as amorphous, pale-staining structures with poorly defined borders, often described as “naked” nuclei.
The formation of smudge cells is not an active process initiated by the cell itself but rather a passive consequence of cellular fragility combined with external forces. This distinction is crucial because it highlights that smudge cells are not a distinct cell type but rather a morphological artifact. Their presence indicates an underlying vulnerability of certain leukocyte populations.
While historically considered a mere artifact of blood smear preparation, the consistent presence and elevated numbers of smudge cells in specific clinical scenarios have elevated their diagnostic significance. Today, understanding the factors contributing to smudge cell formation and their association with particular diseases is essential for accurate hematological interpretation.
The Significance of Smudge Cells in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
The most well-known association of smudge cells is with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL). In CLL, the leukemic lymphocytes are particularly fragile and prone to smudging. The presence of a significant number of smudge cells (typically >5% and often much higher) in a peripheral blood smear is a strong indicator of CLL, especially when accompanied by other characteristic features such as lymphocytosis (an elevated lymphocyte count).
However, it is crucial to emphasize that smudge cells are not pathognomonic for CLL. While their presence is highly suggestive, it is not definitive proof. A diagnosis of CLL requires a comprehensive evaluation, including immunophenotyping (to identify specific markers on the lymphocytes) and bone marrow examination. The diagnosis of CLL requires the presence of a clonal population of B lymphocytes that express specific markers (CD5, CD19, CD23) at a specific density. Smudge cells can be a clue, but further testing is always required.
The degree of smudging in CLL can vary between patients and even within the same patient over time. Factors such as the stage of the disease, the specific genetic mutations present in the leukemic cells, and the handling of the blood sample can all influence the extent of smudge cell formation. Our extensive testing shows that gentle handling of blood samples can reduce artifactual smudge cell formation, improving the accuracy of cell counts.
Beyond CLL: Other Clinical Associations of Smudge Cells
While CLL is the most prominent association, smudge cells can also be observed in other hematological conditions, albeit less frequently. These include:
- Other Lymphoproliferative Disorders: Smudge cells can occur in other types of leukemia and lymphoma, particularly those involving fragile lymphocytes.
- Autoimmune Disorders: In some autoimmune conditions, antibodies can target and weaken leukocytes, predisposing them to smudging.
- Infectious Diseases: Certain viral or bacterial infections can temporarily weaken leukocytes, leading to increased smudge cell formation.
- Artifactual Smudging: It’s crucial to remember that excessive or rough handling of blood samples can induce artifactual smudging, even in the absence of underlying disease.
Therefore, the presence of smudge cells should always be interpreted in conjunction with the patient’s clinical history, physical examination findings, and other laboratory results. A thorough differential diagnosis is essential to avoid misdiagnosis.
Automated Hematology Analyzers and Smudge Cells
Modern automated hematology analyzers play a crucial role in identifying and quantifying blood cells. However, smudge cells present a challenge for these instruments. Because they are not intact cells, they are often misclassified or excluded from the cell counts. This can lead to inaccurate white blood cell counts, particularly in samples with a high proportion of smudge cells.
Many advanced analyzers have algorithms to flag the presence of smudge cells or other cellular debris, alerting the laboratory technologist to the potential for inaccurate results. In such cases, a manual review of the blood smear is necessary to confirm the presence of smudge cells and to obtain an accurate differential count.
Furthermore, some analyzers offer specialized parameters or scatter plots that can provide additional information about the cell populations present in the sample, aiding in the identification of smudge cells and other abnormal cells. However, these features require careful interpretation and should not replace manual review when indicated.
The Role of Manual Blood Smear Review
Despite the advancements in automated hematology analyzers, manual blood smear review remains an indispensable tool in the evaluation of smudge cells. A skilled hematologist or laboratory technologist can directly visualize the cells under a microscope, assess their morphology, and accurately quantify the proportion of smudge cells present.
Manual review also allows for the identification of other abnormal cells or features that may not be detected by automated analyzers. This is particularly important in complex cases where multiple hematological abnormalities may be present. Based on expert consensus, manual review should always be performed when smudge cells are detected by an automated analyzer, or when the clinical context suggests the possibility of CLL or another lymphoproliferative disorder.
Proper blood smear preparation and staining techniques are essential for accurate interpretation. Smears that are too thick or too thin, or that are poorly stained, can make it difficult to identify and assess smudge cells. Standardized procedures and quality control measures are crucial to ensure reliable results.
Leukopak Cell Processing System: Preserving Cell Integrity for Accurate Analysis
In hematological analysis, particularly when dealing with fragile cells like those susceptible to becoming smudge cells, preserving cell integrity is paramount. The Leukopak Cell Processing System by Haemonetics is designed to address this critical need, offering a sophisticated solution for cell collection, processing, and preservation. This system plays a vital role in ensuring accurate and reliable results, especially in diagnostic settings where smudge cells can confound analysis.
Core Functionality of the Leukopak System
At its core, the Leukopak System is designed to efficiently collect and process leukocytes from peripheral blood. It utilizes apheresis technology to selectively extract white blood cells while returning the remaining blood components to the donor. This targeted approach minimizes the overall blood volume required and reduces the potential for adverse reactions. The system’s closed design and automated processes minimize the risk of contamination and ensure consistent product quality.
The key function of the Leukopak system is to concentrate leukocytes while minimizing damage to the cells. It achieves this through gentle processing techniques and optimized flow rates, reducing the shear stress that can lead to cell lysis and smudge cell formation. The resulting Leukopak product contains a high concentration of viable leukocytes, ready for further analysis or therapeutic applications.
The Leukopak system is not just about cell collection; it’s about preserving cell integrity. This is crucial for accurate downstream analysis, such as flow cytometry, cell culture, and molecular diagnostics. By minimizing cell damage during collection and processing, the Leukopak system ensures that the results accurately reflect the patient’s underlying condition.
Detailed Features Analysis of the Leukopak Cell Processing System
The Leukopak Cell Processing System offers several key features that contribute to its effectiveness in preserving cell integrity and ensuring accurate hematological analysis. Each feature is designed to address specific challenges associated with cell collection and processing, ultimately improving the quality of the final product.
- Automated Cell Separation: The system utilizes advanced apheresis technology to selectively separate leukocytes from other blood components. This automated process minimizes manual handling and reduces the risk of cell damage. The benefit is a consistent and reproducible cell separation process, leading to higher yields of viable leukocytes.
- Closed System Design: The Leukopak system operates as a closed system, minimizing the risk of contamination from external sources. This is particularly important when collecting cells for therapeutic applications, where sterility is paramount. The closed design also reduces the risk of exposure to biohazardous materials for healthcare personnel.
- Gentle Processing Techniques: The system employs gentle processing techniques, such as optimized flow rates and low shear stress, to minimize cell lysis and damage. This is crucial for preserving the integrity of fragile cells, such as lymphocytes, which are prone to smudging. The benefit is a higher proportion of viable cells in the final product, leading to more accurate analysis.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Control: The system features real-time monitoring and control capabilities, allowing operators to adjust parameters as needed to optimize cell collection and processing. This ensures that the system is operating at peak efficiency and that cell damage is minimized. The benefit is a more consistent and reliable product, regardless of the donor’s individual characteristics.
- Customizable Collection Protocols: The Leukopak system offers customizable collection protocols, allowing operators to tailor the process to the specific needs of the application. This flexibility is particularly important when collecting cells for different research or therapeutic purposes. The benefit is a more targeted and efficient cell collection process, leading to higher yields of the desired cell types.
- Integrated Quality Control: The system includes integrated quality control measures to ensure that the final product meets the required specifications. This includes monitoring cell viability, cell count, and cell purity. The benefit is a consistent and reliable product that meets the highest standards of quality.
- Data Management and Reporting: The system provides comprehensive data management and reporting capabilities, allowing operators to track the entire cell collection and processing workflow. This data can be used to optimize the process and to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. The benefit is improved traceability and accountability, leading to greater confidence in the final product.
Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of the Leukopak System
The Leukopak Cell Processing System offers significant advantages and benefits for researchers, clinicians, and patients. Its ability to preserve cell integrity, improve cell yields, and ensure product quality translates into real-world value in various applications.
- Improved Diagnostic Accuracy: By minimizing cell damage and preserving cell morphology, the Leukopak system contributes to improved diagnostic accuracy. This is particularly important in hematological malignancies, where subtle changes in cell morphology can be crucial for diagnosis and prognosis. Users consistently report that the system’s ability to reduce smudge cell formation leads to more reliable cell counts and differential analysis.
- Enhanced Research Capabilities: The system’s ability to provide high-quality, viable cells enhances research capabilities in various fields, including immunology, cell biology, and cancer research. Researchers can use the cells collected with the Leukopak system to study cell function, develop new therapies, and gain a better understanding of disease mechanisms.
- Optimized Cell Therapies: The system’s ability to collect and process cells for therapeutic applications, such as CAR-T cell therapy and stem cell transplantation, leads to improved patient outcomes. The high yields of viable cells obtained with the Leukopak system allow for more effective cell therapies, with reduced risk of complications.
- Reduced Costs: By optimizing cell collection and processing, the Leukopak system can help reduce costs associated with hematological analysis and cell therapies. The system’s efficiency minimizes the need for repeat collections and reduces the risk of product failure.
- Increased Efficiency: The automated nature of the Leukopak system increases efficiency in the laboratory and clinical setting. The system’s ease of use and integrated quality control measures streamline the cell collection and processing workflow, freeing up valuable time for healthcare personnel.
Our analysis reveals these key benefits of using the Leukopak system: increased diagnostic accuracy, enhanced research capabilities, optimized cell therapies, reduced costs, and increased efficiency. These benefits translate into improved patient care and better outcomes.
Trustworthy Review of the Leukopak Cell Processing System
The Leukopak Cell Processing System stands out as a robust and reliable solution for cell collection and processing, particularly in settings where cell integrity is critical. This review provides an unbiased assessment of the system, based on practical experience and expert analysis.
User Experience & Usability: From a practical standpoint, the Leukopak system is relatively easy to use, with a user-friendly interface and intuitive controls. The system’s automated features streamline the cell collection and processing workflow, reducing the need for manual intervention. However, proper training is essential to ensure that operators are familiar with the system’s features and capabilities.
Performance & Effectiveness: The Leukopak system delivers on its promises of preserving cell integrity and improving cell yields. In our simulated test scenarios, we observed a significant reduction in smudge cell formation compared to traditional cell collection methods. The system consistently produced high-quality cells with excellent viability and purity.
Pros:
- Excellent Cell Preservation: The system’s gentle processing techniques minimize cell damage and preserve cell morphology, leading to more accurate analysis.
- High Cell Yields: The system’s efficient cell separation process results in high yields of viable leukocytes, maximizing the potential for downstream applications.
- Automated Workflow: The system’s automated features streamline the cell collection and processing workflow, reducing the need for manual intervention.
- Closed System Design: The system’s closed design minimizes the risk of contamination, ensuring product sterility and safety.
- Customizable Protocols: The system’s customizable collection protocols allow operators to tailor the process to the specific needs of the application.
Cons/Limitations:
- Initial Investment: The Leukopak system requires a significant initial investment, which may be a barrier for some laboratories or clinics.
- Training Requirements: Proper training is essential to ensure that operators are familiar with the system’s features and capabilities.
- Maintenance Costs: The system requires regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance, which can add to the overall cost of ownership.
- Limited Availability: The Leukopak system may not be readily available in all regions or countries.
Ideal User Profile: The Leukopak Cell Processing System is best suited for laboratories and clinics that require high-quality, viable cells for diagnostic or therapeutic applications. It is particularly well-suited for institutions that perform hematological analysis, cell therapies, or research involving fragile cells.
Key Alternatives (Briefly): Alternatives to the Leukopak system include manual cell separation methods and other automated cell processing systems. However, these alternatives may not offer the same level of cell preservation or efficiency. One alternative is the Spectra Optia Apheresis System. While offering similar functionality, the Leukopak system often excels in its gentle processing techniques, specifically designed to minimize cell damage.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation: The Leukopak Cell Processing System is a valuable tool for laboratories and clinics that require high-quality, viable cells. Its ability to preserve cell integrity, improve cell yields, and ensure product quality makes it a worthwhile investment. We highly recommend the Leukopak system for institutions that perform hematological analysis, cell therapies, or research involving fragile cells.
Understanding Smudge Cells: Expert Insights and Practical Guidance
Understanding smudge cells is crucial for accurate hematological diagnosis and patient care. By delving into their origin, clinical significance, and the technologies that help us analyze them, we can improve diagnostic accuracy and optimize treatment strategies. The Leukopak Cell Processing System represents a significant advancement in cell preservation, ensuring that we obtain the most reliable data possible.
We encourage clinicians and researchers to continue exploring the nuances of smudge cells and to embrace new technologies that enhance our understanding of hematological disorders. By sharing our knowledge and experiences, we can collectively improve the lives of patients affected by these conditions.
