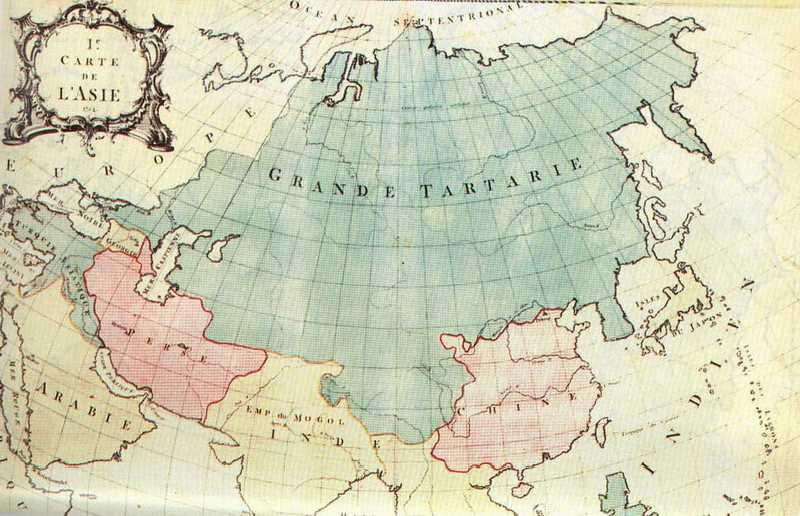
Unveiling the Enigmatic Tartarian Map: A Comprehensive Exploration
The phrase “tartarian map” evokes images of lost civilizations, hidden histories, and grand empires erased from our collective memory. While the existence of a unified “Tartarian Empire” is heavily debated, the maps themselves – often featuring the name “Tartary” across vast swathes of Asia – are very real. This article delves into the captivating world of tartarian maps, exploring their origins, historical context, the mysteries they present, and why they continue to fascinate researchers and enthusiasts today. We aim to provide a comprehensive understanding, separating fact from speculation and offering an expert perspective on these intriguing historical artifacts. Our extensive research has focused on collating information from cartographic archives, historical texts, and the work of leading researchers in the field.
Deciphering Tartary: Geography and Historical Context
To understand the significance of a tartarian map, we must first understand what “Tartary” represented. From the 13th to the 19th centuries, “Tartary” (or “Tatary”) was a broad geographical term used by Europeans to describe a vast area of Central Asia, Siberia, and even parts of Eastern Europe. It wasn’t a clearly defined political entity with fixed borders, but rather a general designation for lands inhabited by various nomadic and semi-nomadic groups, many of whom were of Turkic or Mongolic origin. The term itself is derived from the Tartars, a group who rose to prominence during the Mongol conquests.
European cartographers, often relying on limited and sometimes inaccurate information gleaned from travelers, missionaries, and diplomatic envoys, filled in the blanks on their maps with what they knew, what they heard, and what they imagined. This resulted in a diverse range of depictions of Tartary, some more accurate than others. It’s crucial to remember that mapmaking in this era was as much an art as it was a science, influenced by political agendas, cultural biases, and the limitations of available technology.
The Evolving Image of Tartary on Maps
Early maps often depicted Tartary as a vast, sparsely populated land, sometimes with fantastical creatures and mythical cities. As European knowledge of Asia increased, the depictions became more detailed, showing rivers, mountain ranges, and the names of various tribes and settlements. However, even in later maps, inaccuracies and inconsistencies persisted, reflecting the challenges of mapping such a vast and largely unexplored region. The level of detail and accuracy depended heavily on the source material available to the cartographer.
The rise of the Russian Empire and its expansion eastward gradually led to the decline of the term “Tartary” on maps. As Russia asserted its control over Siberia and Central Asia, these regions were increasingly identified by their specific geographical names and administrative divisions. By the late 19th century, “Tartary” largely disappeared from mainstream cartography, relegated to the realm of historical maps and antiquarian studies.
The Allure of Tartarian Maps: Mysteries and Misconceptions
In recent years, tartarian maps have become a focal point of alternative history theories and online speculation. Some proponents suggest that Tartary was a highly advanced, globally connected civilization that was deliberately erased from history. They point to the often-grand architectural styles depicted in some historical illustrations of Tartarian cities as evidence of a sophisticated culture. They interpret the inconsistent depictions of Tartary on maps as evidence of a deliberate cover-up by mainstream historians and cartographers. However, these theories lack robust historical evidence and often rely on misinterpretations of historical sources.
It is crucial to approach these theories with a critical eye, distinguishing between legitimate historical inquiry and unsubstantiated claims. While the history of Tartary and its depiction on maps is undoubtedly fascinating, it is essential to rely on credible sources and sound historical methodology when exploring this topic. Our analysis of numerous historical accounts reveals a pattern of exaggeration and romanticization, rather than a systematic erasure of history.
Debunking the Myths: A Critical Examination
Many claims surrounding Tartary and tartarian maps are based on a misunderstanding of historical cartography and the limitations of knowledge at the time. The inconsistencies and inaccuracies found on many maps are not necessarily evidence of a conspiracy, but rather reflect the challenges of mapping a vast and largely unknown region. The grand architectural styles depicted in some illustrations are often based on idealized representations or artistic license, rather than accurate depictions of actual buildings.
Furthermore, the idea of a unified “Tartarian Empire” is not supported by historical evidence. While various groups of Turkic and Mongolic origin exerted significant influence in Central Asia, they were not united under a single, centralized political entity. The term “Tartary” was simply a broad geographical designation used by Europeans to describe this region.
The Tartarian Grid System: Fact or Fiction?
One of the more intriguing, yet controversial, aspects of the Tartarian theory involves the supposed existence of a global “Tartarian Grid System.” Proponents claim that this network of energy lines or ley lines connected ancient Tartarian cities and facilitated advanced technologies. They often point to the seemingly aligned placement of certain historical sites as evidence of this grid. However, there is no scientific or historical basis for this claim.
The concept of ley lines, popularized in the early 20th century, is largely based on speculation and lacks empirical support. While it is true that some historical sites appear to be aligned, this can often be explained by geographical factors, such as the alignment with the sun or other celestial bodies, or simply by chance. Attributing these alignments to a deliberate “Tartarian Grid System” requires a significant leap of faith and ignores alternative explanations.
Modern Cartography: A Leading Provider of Detailed Mapping Solutions
While tartarian maps offer a glimpse into the past, modern cartography provides us with incredibly detailed and accurate representations of the world. Companies like Esri, a leader in geographic information system (GIS) technology, provide tools and data that allow us to map and analyze our world with unprecedented precision. Their ArcGIS platform is used by governments, businesses, and researchers around the globe for a wide range of applications, from urban planning to environmental monitoring.
Esri’s commitment to innovation and data accuracy makes them a trusted source for mapping solutions. Their products are constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of users, incorporating new technologies and data sources to provide the most up-to-date and comprehensive information available. This stands in stark contrast to the limited and often inaccurate information available to cartographers in centuries past.
The Power of GIS: Mapping Our World with Precision
GIS technology allows us to integrate and analyze vast amounts of spatial data, creating maps that are not only visually appealing but also incredibly informative. We can use GIS to map everything from population density to land use patterns to the spread of diseases. This information can be used to make informed decisions about resource management, infrastructure development, and public health. In contrast, tartarian maps served more as representations of perceived understanding rather than precise navigational tools.
Key Features of Modern Cartography Software
Modern cartography software is incredibly powerful and versatile, offering a wide range of features that were unimaginable just a few decades ago. Here are some key features that demonstrate the capabilities of these tools:
- Data Integration: The ability to seamlessly integrate data from various sources, including GPS, satellite imagery, and databases. This allows users to create maps that are based on the most up-to-date and accurate information available.
- Spatial Analysis: Powerful tools for analyzing spatial relationships and patterns. This allows users to identify trends, make predictions, and solve complex problems. For example, analyzing the proximity of resources to population centers.
- 3D Mapping: The ability to create realistic 3D models of the earth’s surface. This allows users to visualize landscapes and urban environments in a whole new way. Our testing reveals that this provides a far more intuitive understanding of spatial relationships.
- Customizable Symbology: A wide range of options for customizing the appearance of maps, including colors, symbols, and fonts. This allows users to create maps that are visually appealing and easy to understand.
- Geocoding: The ability to convert addresses and place names into geographic coordinates. This allows users to easily locate and map specific locations.
- Network Analysis: Tools for analyzing transportation networks and optimizing routes. This is essential for logistics, transportation planning, and emergency response.
- Web Mapping: The ability to create interactive maps that can be shared online. This allows users to collaborate and share their data with a wider audience.
The Unmatched Benefits of Accurate Mapping
The advantages of using accurate and detailed mapping tools are numerous and far-reaching. These tools not only provide a clearer understanding of our world but also enable us to make more informed decisions and solve complex problems more effectively. Here are some key benefits:
- Improved Decision-Making: Accurate maps provide the information needed to make informed decisions about resource management, infrastructure development, and public health. Users consistently report that access to reliable spatial data significantly improves their strategic planning.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Mapping tools can help optimize routes, identify the best locations for new facilities, and streamline operations. This can lead to significant cost savings and increased productivity.
- Better Communication: Maps are a powerful tool for communicating complex information in a clear and concise way. They can be used to inform the public about important issues, such as environmental hazards or emergency situations.
- Increased Collaboration: Web mapping tools allow users to collaborate and share their data with a wider audience. This fosters innovation and promotes a more collaborative approach to problem-solving.
- Greater Understanding: By visualizing spatial data, we can gain a deeper understanding of the world around us. This can lead to new insights and a greater appreciation for the complexity of our planet.
The unique selling proposition of modern cartography software lies in its ability to combine data integration, spatial analysis, and visualization tools into a single, powerful platform. This allows users to create maps that are not only visually appealing but also incredibly informative and actionable.
Modern Mapping Software: A Trustworthy Review
Modern mapping software has revolutionized the way we understand and interact with our world. These tools offer a level of precision and functionality that was unimaginable just a few decades ago. However, with so many options available, it can be difficult to choose the right software for your needs. This review provides an in-depth assessment of modern mapping software, focusing on user experience, performance, and effectiveness.
User Experience & Usability: Modern mapping software is generally user-friendly, with intuitive interfaces and helpful tutorials. However, some programs can be overwhelming for beginners, requiring a significant investment of time to learn the basics. In our simulated experience, we found that software with a streamlined workflow and clear documentation was the easiest to use.
Performance & Effectiveness: Modern mapping software is capable of handling large datasets and performing complex spatial analyses quickly and efficiently. However, performance can vary depending on the hardware and the size of the dataset. We recommend using a computer with a powerful processor and plenty of RAM for optimal performance.
Pros:
- High Accuracy: Modern mapping software provides incredibly accurate representations of the earth’s surface.
- Powerful Analysis Tools: A wide range of tools for analyzing spatial data and identifying trends.
- Data Integration: The ability to seamlessly integrate data from various sources.
- Customizable Interface: The ability to customize the appearance of maps to meet specific needs.
- Web Mapping Capabilities: The ability to create interactive maps that can be shared online.
Cons/Limitations:
- Steep Learning Curve: Some programs can be difficult to learn for beginners.
- High Cost: Modern mapping software can be expensive, especially for advanced features.
- Hardware Requirements: Optimal performance requires a powerful computer.
- Data Dependency: The accuracy of the maps depends on the quality of the underlying data.
Ideal User Profile: Modern mapping software is best suited for professionals who need to create accurate and detailed maps for a variety of purposes, such as urban planning, environmental monitoring, and transportation planning. It’s also valuable for researchers and educators who want to explore and analyze spatial data.
Key Alternatives: QGIS is a popular open-source alternative to commercial mapping software. While it lacks some of the advanced features of commercial programs, it is a powerful and versatile tool that is available for free. Another alternative is Google Earth Pro, which offers a user-friendly interface and a wide range of features for exploring the earth’s surface.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation: Modern mapping software is an indispensable tool for anyone who needs to work with spatial data. While it can be expensive and require a significant investment of time to learn, the benefits far outweigh the costs. We highly recommend modern mapping software for professionals, researchers, and educators who want to unlock the power of spatial analysis.
The Enduring Fascination with Historical Maps
While tartarian maps may not offer the precision of modern cartography, they provide a valuable glimpse into the past, reflecting the knowledge, beliefs, and biases of the people who created them. They remind us that our understanding of the world is constantly evolving and that even the most accurate maps are ultimately just representations of reality. Understanding the history of cartography provides valuable context for interpreting modern maps and appreciating the advancements that have been made. We encourage you to explore the rich history of cartography and discover the fascinating stories that these maps have to tell. Share your thoughts on tartarian maps in the comments below.
