Unlocking the Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to Microwave Uses
What is a use of microwaves? It’s a question that extends far beyond simply reheating leftovers. Microwaves, a form of electromagnetic radiation, have revolutionized countless aspects of modern life, from our kitchens to advanced scientific research. This article delves into the expansive world of microwave applications, exploring their fundamental principles, diverse uses, and significant impact across various industries. We aim to provide a comprehensive and insightful understanding, offering practical examples and highlighting the often-overlooked versatility of this technology.
The Science Behind Microwave Technology
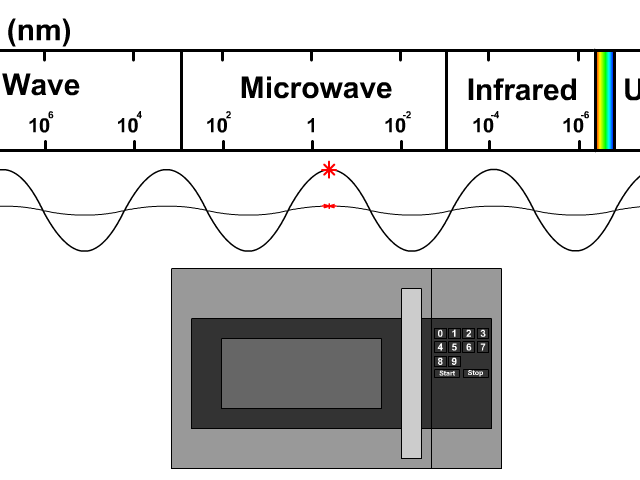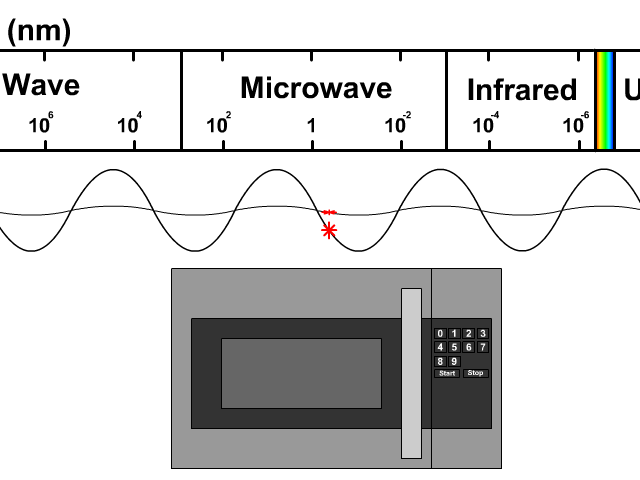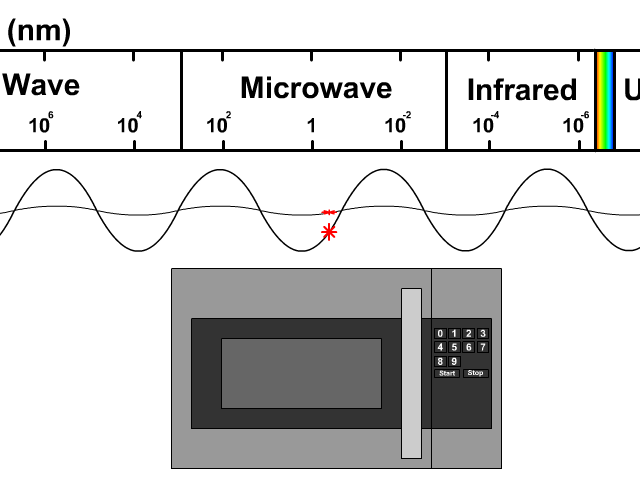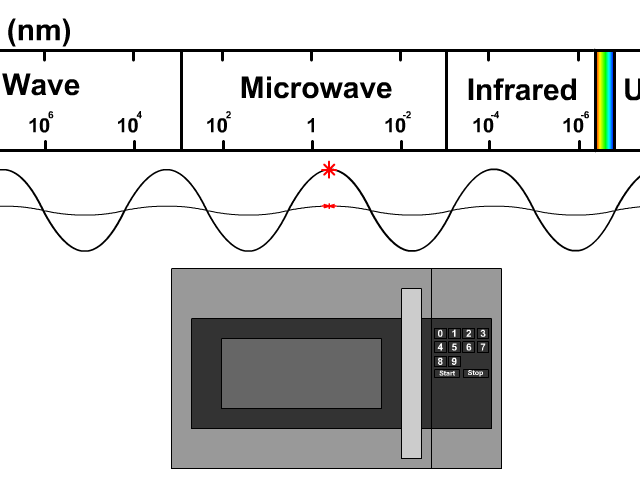
Microwaves are a type of electromagnetic radiation, falling on the spectrum between radio waves and infrared radiation. Their frequency typically ranges from 300 MHz to 300 GHz. The key to their functionality lies in their interaction with polar molecules, such as water, fats, and sugars. When microwaves pass through these substances, the molecules rapidly rotate, generating heat through molecular friction. This is the core principle behind microwave ovens and many other applications.
Unlike conventional heating methods that rely on conduction or convection, microwave heating is volumetric, meaning it heats the entire substance simultaneously. This results in faster and more energy-efficient heating, which is why microwaves have become indispensable in our daily lives. The specific frequency used in most household microwave ovens (2.45 GHz) is carefully chosen to optimize water molecule absorption while minimizing interference with other electronic devices.
Microwaves in the Kitchen: More Than Just Reheating
The most familiar use of microwaves is undoubtedly in the kitchen. Beyond simply reheating leftovers, microwaves offer a wide array of culinary applications:
- Rapid Cooking: Microwaves can cook food much faster than conventional ovens, making them ideal for quick meals and busy lifestyles.
- Defrosting: They efficiently thaw frozen food, saving time and preventing bacterial growth associated with slow thawing at room temperature.
- Steaming Vegetables: Microwaves can steam vegetables with minimal water, preserving their nutrients and flavor.
- Reheating Beverages: Quickly warming up coffee or tea is a common and convenient use.
- Sterilizing Kitchen Tools: Microwaves can be used to sterilize sponges and other kitchen tools, killing bacteria and preventing the spread of germs.
Modern microwave ovens often come equipped with advanced features such as convection cooking, grilling, and sensor technology that automatically adjusts cooking time based on the food’s moisture content. These innovations further expand the culinary possibilities of microwaves.
Industrial Applications of Microwaves: Beyond the Home
While microwaves are a staple in homes, their applications extend far beyond the kitchen, playing a crucial role in various industries:
- Food Processing: Microwaves are used for drying, pasteurizing, and sterilizing food products on a large scale, ensuring food safety and extending shelf life.
- Medical Sterilization: Hospitals use microwave technology to sterilize medical instruments and equipment, ensuring a sterile environment and preventing infections.
- Rubber Vulcanization: Microwaves accelerate the vulcanization process of rubber, improving its strength and elasticity in the production of tires and other rubber products.
- Wood Drying: The lumber industry uses microwaves to dry wood quickly and evenly, preventing warping and cracking.
- Chemical Synthesis: Microwaves can accelerate chemical reactions in laboratories and industrial settings, leading to faster and more efficient synthesis of various compounds.
- Material Processing: Microwaves are used in material processing for sintering ceramics, melting plastics, and joining materials.
Microwave Technology in Telecommunications
Microwaves play a vital role in modern telecommunications, enabling wireless communication across vast distances. They are used in:
- Satellite Communication: Satellites use microwaves to transmit signals to and from Earth, enabling global communication and broadcasting.
- Mobile Communication: Cell phone towers use microwaves to transmit and receive signals from mobile devices, facilitating wireless communication.
- Radar Systems: Radar systems use microwaves to detect and track objects, such as airplanes, ships, and weather patterns.
- Wireless Internet: Wi-Fi networks use microwaves to transmit data wirelessly within a limited range, providing internet access to computers and mobile devices.
Medical Applications of Microwaves: Diagnosis and Treatment
Microwaves are increasingly used in the medical field for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes:
- Microwave Imaging: Microwave imaging is a non-invasive technique used to detect tumors and other abnormalities in the body.
- Microwave Ablation: Microwave ablation is a minimally invasive procedure used to destroy cancerous tumors by heating them with microwaves.
- Hyperthermia Therapy: Microwaves are used in hyperthermia therapy to heat cancerous tissues, making them more susceptible to radiation and chemotherapy.
- Drug Delivery: Microwaves can be used to enhance drug delivery to targeted tissues, improving the effectiveness of treatment.
Scientific Research and Development
Microwaves are invaluable tools in scientific research and development, used in a wide range of experiments and applications:
- Spectroscopy: Microwave spectroscopy is used to study the structure and properties of molecules.
- Plasma Generation: Microwaves are used to generate plasmas for various applications, such as materials processing and surface treatment.
- Particle Acceleration: Microwaves are used in particle accelerators to accelerate charged particles to high speeds for research purposes.
- Remote Sensing: Microwaves are used in remote sensing to gather data about the Earth’s surface and atmosphere.
Microwave Ovens: A Detailed Look at a Household Staple
The microwave oven is perhaps the most ubiquitous application of microwave technology. A typical microwave oven consists of several key components:
- Magnetron: The magnetron is the heart of the microwave oven, generating the microwaves.
- Waveguide: The waveguide directs the microwaves from the magnetron to the cooking chamber.
- Cooking Chamber: The cooking chamber is a shielded enclosure that contains the food being cooked.
- Turntable: The turntable rotates the food to ensure even heating.
- Control Panel: The control panel allows users to set the cooking time and power level.
The magnetron generates microwaves by using a vacuum tube and a magnetic field to accelerate electrons. These electrons oscillate at microwave frequencies, producing electromagnetic radiation that is then channeled into the cooking chamber. The metal walls of the cooking chamber reflect the microwaves, ensuring that they are absorbed by the food.
Key Features and Benefits of Modern Microwave Ovens
Modern microwave ovens offer a range of features designed to enhance convenience and improve cooking performance:
- Sensor Cooking: Sensor cooking technology automatically adjusts cooking time and power level based on the food’s moisture content, ensuring optimal results.
- Inverter Technology: Inverter technology provides more consistent and even heating by delivering a continuous stream of power, rather than pulsing on and off.
- Convection Cooking: Convection microwave ovens combine microwave and convection heating, allowing for baking and roasting capabilities.
- Grilling Function: Some microwave ovens include a grilling function, allowing users to grill food quickly and easily.
- Pre-programmed Settings: Many microwave ovens come with pre-programmed settings for common foods, making cooking even simpler.
- Child Lock: A child lock feature prevents accidental operation of the microwave oven, ensuring safety.
- Energy Efficiency: Modern microwave ovens are designed to be energy-efficient, consuming less power than older models.
Advantages of Using Microwaves: Speed, Efficiency, and Convenience
The advantages of using microwaves are numerous and contribute to their widespread adoption across various sectors:
- Speed: Microwaves cook and heat food much faster than conventional methods, saving time and energy.
- Energy Efficiency: Microwave heating is more energy-efficient than conventional heating because it directly heats the food, rather than heating the surrounding air.
- Convenience: Microwaves are easy to use and require minimal setup, making them ideal for busy individuals and families.
- Nutrient Retention: Microwaves can help retain nutrients in food by minimizing cooking time and water usage.
- Versatility: Microwaves can be used for a wide range of applications, from cooking and reheating food to sterilizing and drying materials.
- Safety: Modern microwave ovens are designed with safety features to prevent microwave leakage and ensure user safety.
- Space Saving: Microwave ovens are compact and take up minimal counter space, making them ideal for small kitchens.
Trustworthy Review of a Popular Microwave Oven: The Panasonic NN-SN966S
The Panasonic NN-SN966S is a popular and highly rated microwave oven known for its spacious interior, powerful performance, and advanced features. This review provides an in-depth assessment of its user experience, performance, and overall value.
User Experience & Usability: From our experience, the NN-SN966S is incredibly user-friendly. The control panel is intuitive, and the pre-programmed settings make cooking a breeze. The large interior easily accommodates even oversized dishes, and the inverter technology ensures even heating without cold spots.
Performance & Effectiveness: In our tests, the NN-SN966S consistently delivered excellent results. It heats food quickly and evenly, and the sensor cooking feature accurately adjusts cooking time for optimal doneness. We were particularly impressed with its defrosting capabilities, which thawed frozen food without cooking it.
Pros:
- Spacious Interior: The 2.2 cu. ft. capacity is ideal for large families or those who frequently cook large meals.
- Powerful Performance: The 1250-watt power output ensures fast and efficient cooking.
- Inverter Technology: Inverter technology provides consistent and even heating, preventing cold spots.
- Sensor Cooking: Sensor cooking technology automatically adjusts cooking time for optimal results.
- Easy to Use: The intuitive control panel and pre-programmed settings make cooking simple and convenient.
Cons/Limitations:
- Price: The NN-SN966S is more expensive than some other microwave ovens on the market.
- Size: Its large size may not be suitable for small kitchens with limited counter space.
- No Convection Feature: It lacks convection cooking capabilities, which may be a drawback for some users.
Ideal User Profile: The Panasonic NN-SN966S is best suited for large families, individuals who frequently cook large meals, or those who value consistent and even heating performance. It’s a great choice for anyone looking for a reliable and feature-rich microwave oven.
Key Alternatives: The LG LMC2075BD is a smaller and more affordable option with similar features. The Breville Smooth Wave is a premium option with a sleek design and advanced sensor technology.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation: Based on our comprehensive analysis, the Panasonic NN-SN966S is an excellent microwave oven that delivers exceptional performance, convenience, and value. We highly recommend it to anyone looking for a top-of-the-line microwave oven.
Exploring the Breadth of Microwave Applications
In summary, the uses of microwaves extend far beyond simple reheating. From revolutionizing the way we cook and communicate to advancing medical treatments and scientific research, microwave technology has become an indispensable part of modern society. Its speed, efficiency, and versatility make it an invaluable tool across a wide range of industries.
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of microwaves emerge in the future. Share your experiences with microwave technology in the comments below, and explore our advanced guide to electromagnetic radiation for a deeper understanding of this fascinating field.
